+86-371-64259555
+86-371-64259555
Coaxial cable is a type of electrical cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield.

APPLICATIONS:
Coaxial cable is used as a transmission line for radio frequency signals. Its applications include feedlines connecting radio transmitters and receivers with their antennas, computer network (Internet) connections, digital audio (S/PDIF), and distributing cable television signals. One advantage of coaxial over other types of radio transmission cable is that in an ideal coaxial cable the electromagnetic field carrying the signal exists only in the space between the inner and outer conductors. This allows coaxial cable runs to be installed next to metal objects such as gutters without the power losses that occur in other types of transmission lines. Coaxial cable also provides protection of the signal from external electromagnetic interference.
The characteristic impedance of the cable is determined by the dielectric constant of the inner insulator and the radii of the inner and outer conductors. A controlled cable characteristic impedance is important because the source and load impedance should be matched to ensure maximum power transfer and minimum standing wave ratio. Other important properties of coaxial cable include attenuation as a function of frequency, voltage handling capability, and shield quality.
Coaxial cable design choices affect physical size, frequency performance, attenuation, power handling capabilities, flexibility, strength, and cost. The inner conductor might be solid or stranded; stranded is more flexible. To get better high-frequency performance, the inner conductor may be silver-plated. Copper-plated steel wire is often used as an inner conductor for cable used in the cable TV industry.
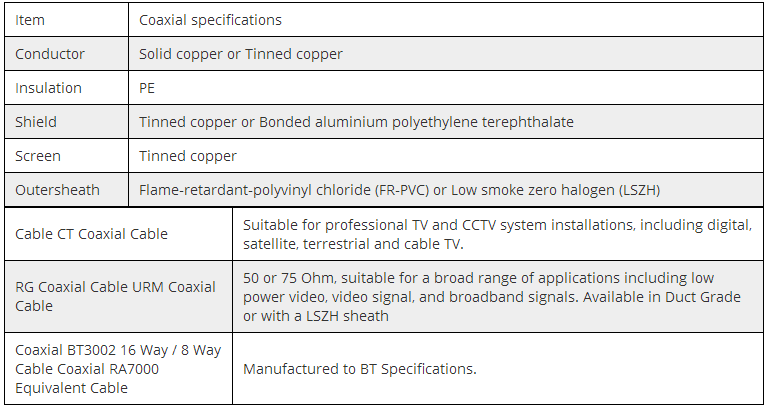
COAXIAL CABLE TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
Leave Comment